Act FAST - Stroke
On Monday 4th November, NHS England is launching the latest ‘Act FAST’ campaign. It aims to increase knowledge of the signs of a stroke and encourage people to dial 999 immediately in response to any sign – even if it doesn’t seem like much. Earlier recognition of symptoms and immediate action enables faster access to specialist treatment and the best chance of reducing long-term effects such as disability.
Stroke symptoms can be less dramatic, painful or obvious than expected, which can lead to a delay in people calling 999, while they wait to see if symptoms progress or improve.
The main symptoms of stroke are face weakness, arm weakness and speech problems. A new TV advert shows an example of each symptom: struggling to smile (face), not being able to raise your arm (arm) or slurring when you speak (speech). The advert explains that although these might not seem like much, any sign of a stroke is always an emergency. By showing different people experiencing a single symptom, the advert is designed to show the importance of dialling 999 immediately in response to any sign of a stroke, rather than waiting to see if symptoms worsen or multiple symptoms develop.
The new campaign builds on the success of the previous Act FAST campaign using an updated call to action: ‘Face or Arm or Speech, at the first sign, it’s Time to call 999’.
The campaign will run in England across TV, TV on demand, radio, social media, national press and ethnic minority TV and radio stations. The campaign also includes specific communications for multicultural and disabled audiences.
This phase of the ‘Help Us Help You’ campaign will run from 4th November until 15th December 2024.
The primary audiences of the campaign are those most at risk of stroke: people over the age of 50, with a focus on C2DE socio-economic groups and Black and South Asian audiences. The campaign will highlight the importance of immediately calling 999, which is also relevant to a wider all-adult audience of ‘stroke savers’, who may witness somebody showing a stroke symptom, be it a loved one or a friend.
Stroke statistics
- Around 100,000 stroke happen each year in the UK
- Around 34,000 death per year in the UK as a result of Stroke
- Fourth single leading cause of death in the UK
- Around 1.9millions nerve cells in the brain are lost every minute a stroke is left untreated, which is why it is so important to act FAST
- If left untreated a Stroke can result in permanent disability or death
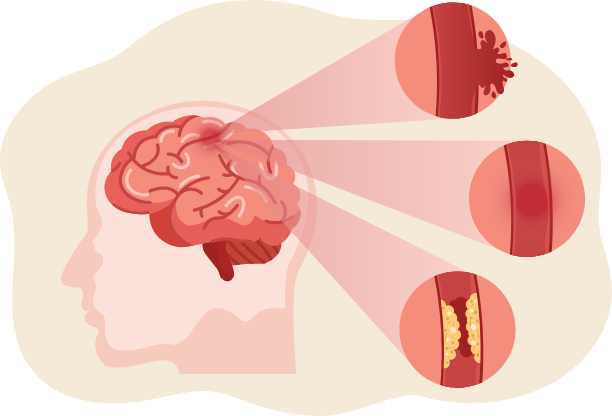
Different types of Strokes
Ischaemic Stroke – this is the most common type of stroke, this is when the blood supply is cut off to part of the brain
Haemorrhagic Stroke – this is caused by bleeding around the brain
Transient Ischaemic Stroke (TIA) – this is also know as a mini stroke, the symptoms of this are often temporary because the blockage stopping blood get to the brain is only temporary.
What are the symptoms of a Stroke?
Stroke can happen to anyone at anytime, and it is really important to know the signs to enable to fast effective treatment. The sooner a stroke is treated the better chance of survival and recovery.
Common symptoms include:
- Face – has the persons face drooped? Can they smile? Arm
- Weakness – can the person raise both arms? Is the person experiencing sudden weakness in their arm or one side of body?
- Speech – has the persons speech changed? Can you understand them?
- Confusion – is the person experiencing confusion such as memory loss, dizziness and/or sudden falls?
- Vision – is the person experiencing blurred or loss of vision in one or both eyes? Does the person have a sudden headache that is severe?
If you see any of these sign, call 999 immediately.

What can increase my risk of having a stroke?
There are many factors that contribute to a stroke, including:
- Smoking
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Physical inactivity
- Being overweight
- Conditions such as Diabetes, High Blood Pressure, High Cholesterol and Atrial Fibrillation
What can I do reduce my risk of having a stroke?
Thankfully many of the factors that increase the risk of stroke can be reduced through simple lifestyle changes, such as:
- Quitting smoking
- Limit your alcohol intake
- Becoming more active each day
- Eating a healthy balanced diet, avoiding foods with high salt and saturated fats
- Monitor you Blood Pressure at home – taking your Blood pressure at home is easy and can help to detect raised blood pressure. Left undetected high blood pressure can lead to heart attack or stroke. To learn more about Blood pressure click here
To learn more about simple effective lifestyle changes you can make to reduce the risk of stroke, visit our lifestyle page here
What happens following a Stroke?
Following Stroke, some people may have long-term side affects and require rehabilitation support to help them make the best possible recovery. Rehabilitation often starts in hospital and will continue following your discharge home or into a community setting. Rehabilitation will be dependent upon your individual circumstances and be tailored to your needs.
Depending upon your needs a team of specialists may support you with your rehabilitation following a stroke including:
- Physiotherapists – support you to regain your strength and movement following a stroke
- Occupational Therapists – support you to re-learn every day activities to help you return to your normal life following a stroke
- Speech & Language Therapists – support patients if they are having difficulties with their speech, and issues with eating and swallowing
- Social Work support – work with the patient, family & carers to set & achieve realistic goals based on the patients needs.